Air Balancing Demystified
A Facility Manager's Essential Guide
Maintaining consistent comfort and efficiency across multiple commercial locations is a top priority for facility managers. Air balancing is a critical yet often overlooked process that ensures your HVAC system delivers optimal performance. This article breaks down what air balancing entails, why it matters, and how it impacts your operations, while incorporating the latest industry best practices and standards.
What Is Air Balancing?
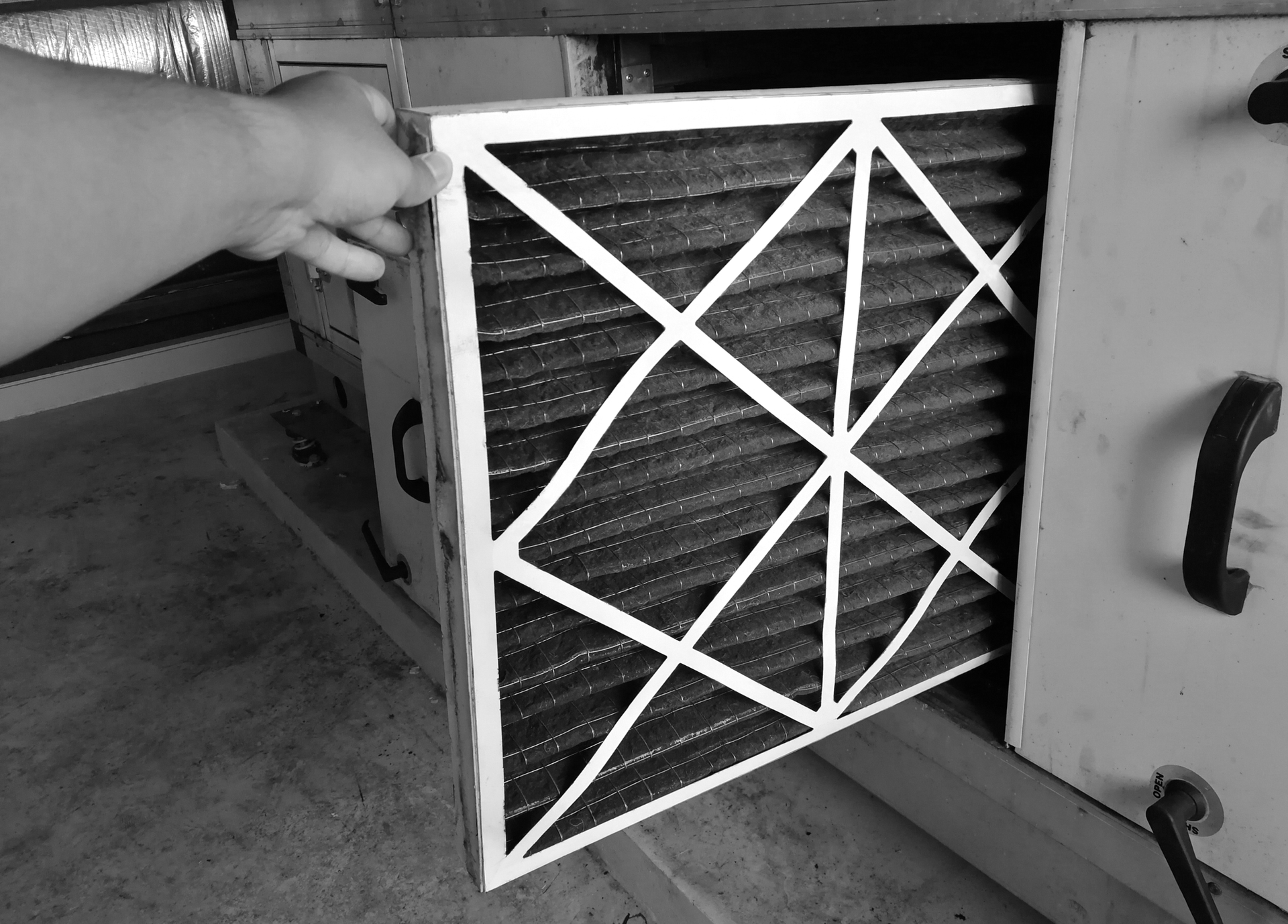
Air balancing is the process of testing, adjusting, and coordinating an HVAC system to ensure even airflow distribution throughout a building. Proper air balancing ensures that each room or zone receives the correct amount of air, maintaining consistent temperatures and improving system performance1. It involves measuring airflow rates, temperature, and pressure at vents using specialized tools like velocity meters, micromanometers, and hood flow meters, then making precise adjustments to dampers, fans, and ducts. The process is systematic and documented, ensuring the system operates as designed and meets both comfort and efficiency goals.
Effective air balancing is essential for efficient heat transfer and conditioning in all intended zones. If airflow across an evaporator coil or through ductwork is inadequate, some rooms may never reach their target temperature, leading to persistent comfort complaints.
Why Air Balancing Matters for Commercial Spaces
- Comfort Consistency: Eliminates hot/cold spots and ensures uniform temperatures. Improper air balancing is a common root cause of rooms that struggle to stay cool or warm, even when the HVAC equipment is functioning correctly1.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces wasted energy from overworked equipment, potentially saving 15–25% in energy use. An improperly balanced system can cause severe energy inefficiencies, as negative pressure or infiltration from unconditioned air increases the load on heating and cooling equipment2.
- Equipment Longevity: Minimizes wear and tear by reducing system strain, as the HVAC equipment doesn’t need to compensate for airflow deficiencies.
- Indoor Air Quality: Promotes effective contaminant removal and balanced humidity levels. If a building is negatively balanced, it may draw in unfiltered air from undesirable sources, which can compromise air quality and even food safety in certain settings.
- Operational Reliability: Prevents issues like drafts, foggy windows, and pressure imbalances that can disrupt building function. Maintaining a neutral or slightly positive building pressure through proper air balancing helps avoid infiltration of outdoor air, which can lead to temperature and humidity issues.
When to Schedule Air Balancing
- At Initial Installation: Air balancing should always be performed when a new HVAC system is installed. This ensures the system is delivering the designed airflow to every area before the building is occupied.
- After Major Modifications or Renovations: If significant changes are made to the building layout or HVAC system-such as moving walls, adding rooms, or upgrading equipment-schedule air balancing to recalibrate airflow and maintain comfort and efficiency.
- When Occupants Report Comfort Issues: If you receive complaints about hot/cold spots, drafts, stuffy air, or uneven temperatures, it’s a clear sign the system may need balancing. Addressing these issues promptly can restore comfort and prevent further problems.
- Periodically as Preventive Maintenance: Even without noticeable issues, regular air balancing is recommended. For most commercial buildings, this means at least once a year, though every two to three years may suffice for less complex or lower-occupancy facilities. High-traffic or frequently reconfigured spaces may require more frequent checks.
- When System Performance Declines: If you notice unexplained increases in energy bills, reduced airflow, excessive humidity, or other signs of inefficiency, air balancing can help diagnose and correct underlying issues before they escalate.
- Before Functional Performance Testing: For new construction or major renovations, air balancing is a prerequisite for functional performance testing and final commissioning, ensuring all systems operate as intended before occupancy.
The Air Balancing Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
- System Assessment: Review ductwork, equipment specs, and building layout to identify potential issues. Airflow must be evaluated not just at the equipment but throughout the entire duct system, as deficiencies are often found in distribution, not just in the HVAC unit itself.
- Measurement: Use precision tools to gather data on airflow, pressure, and temperature at each vent and return. Technicians rely on airflow hoods, anemometers, and manometers to ensure accuracy.
- Adjustment: Calibrate dampers, fan speeds, and controls to correct imbalances and achieve design specifications. Adjustments are made until each room or zone receives the correct amount of air, as measured against design targets or manufacturer recommendations.
- Verification and Documentation: Re-test the system to confirm balanced airflow, proper pressure, and temperature consistency. Document all results in a comprehensive air balance report, which serves as proof that the system meets specifications and provides a reference for future maintenance. This report typically includes project details, system layout, test results, and any deficiencies found.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Schedule periodic rebalancing and monitor system performance to maintain optimal conditions over time. As building use or occupancy changes, rebalancing ensures continued comfort and efficiency.
Government and Industry Guidelines
The ENERGY STAR HVAC Commissioning Checklist and industry standards stress the importance of balancing dampers, verifying airflow with calibrated tools, and maintaining thorough documentation. Adhering to these guidelines can reduce HVAC-related energy use by up to 18% and ensure compliance with codes and best practices3.
Choosing the Right Professionals
Hire certified TAB (Testing, Adjusting, Balancing) professionals with experience in commercial and multi-site systems. Ensure they provide detailed documentation and follow industry standards for safety and accuracy. The expertise of the technician is crucial-proper air balancing is a specialized skill that requires both technical knowledge and attention to detail.
Conclusion
Air balancing is an essential, ongoing strategy for maintaining comfort, efficiency, and reliability in commercial buildings. By following a systematic, well-documented process and partnering with qualified professionals, facility managers can proactively address airflow issues, reduce costs, and protect their HVAC investment for the long term. Achieving harmony in your HVAC system through proper air balancing is key to delivering the comfort and performance your occupants expect.
Have you ever dealt with hot and cold spots in your facilities, or had to troubleshoot airflow issues? Share your questions, insights, or lessons learned in the comments below — we’d love to hear from facility professionals!
Resources:
1 https://www.achrnews.com/articles/163882-air-balancing-achieving-harmony-in-an-hvac-system
2 https://www.achrnews.com/articles/157370-the-importance-of-facility-air-balance